Ejercicios de past perfect simple y past perfect continuous
En esta guía encontrarás una explicación clara, ejemplos y ejercicios de past perfect simple y past perfect continuous para practicar en contexto real. Está pensada para alumnos intermedios y avanzados que quieran dominar el contraste entre ambos tiempos y evitar errores frecuentes.
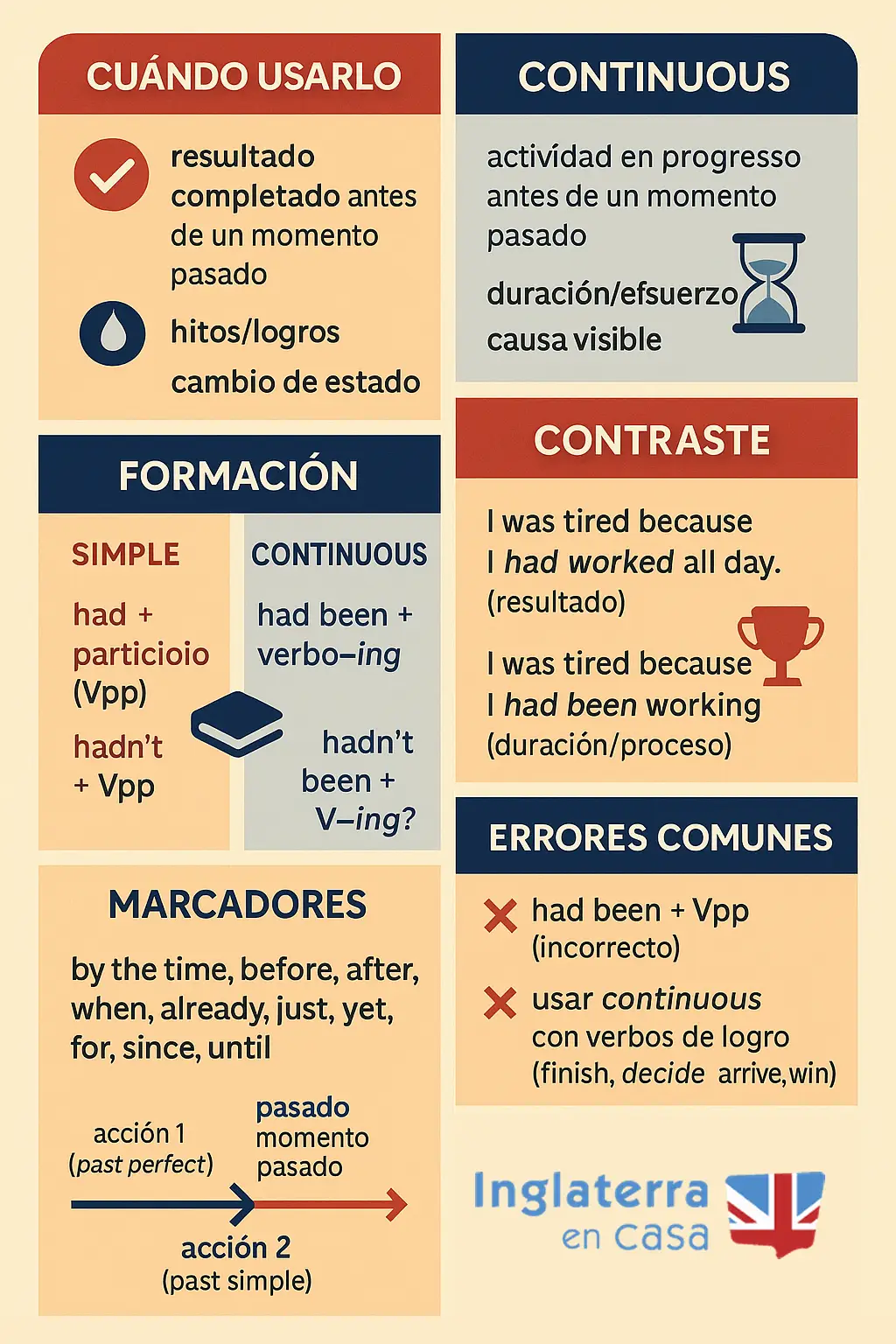
1) Recordatorio rápido: significado y uso
Past Perfect Simple (had + past participle)
Se usa para hablar de una acción terminada antes de otro momento pasado. Enfatiza el resultado o el hecho de estar completada.
Ejemplo: By the time the class started, the teacher had prepared all the materials.
Past Perfect Continuous (had been + -ing)
Se usa para hablar de una actividad en progreso antes de otro momento pasado. Enfatiza la duración, el proceso o el desgaste que provoca.
Ejemplo: The students had been studying for two hours when the exam finally began.
2) Diferencia clave en una frase
Past Perfect Simple: I was tired because I had worked all day. (Trabajo completado antes de estar cansado).
Past Perfect Continuous: I was tired because I had been working all day. (Proceso/actividad prolongada que causa el cansancio).
3) Formación
Affirmative
Past Perfect Simple: Subject + had + Vpp → She had finished.
Past Perfect Continuous: Subject + had been + V-ing → She had been finishing.
Negative
Simple: Subject + had not (hadn’t) + Vpp → They hadn’t arrived.
Continuous: Subject + had not (hadn’t) been + V-ing → They hadn’t been waiting.
Interrogative
Simple: Had + subject + Vpp? → Had you finished?
Continuous: Had + subject + been + V-ing? → Had you been waiting?
4) Marcadores temporales útiles
before, by the time, when, after, until, for, since, just, already, yet.
Con for/since es frecuente el continuous para destacar duración: They had been rehearsing for three hours by the time the show started.
5) Cuándo usar cada uno
Past Perfect Simple: acciones puntuales o completadas; cambio de estado; logro de un objetivo (“had finished, had left, had decided”).
Past Perfect Continuous: actividades largas o repetidas que conducen a una consecuencia; énfasis en esfuerzo, causa o duración (“had been working, had been raining”).
INFOGRAFÍA
UN POCO DE HUMOR

6) Ejercicios de práctica
A) Opción múltiple (elige la mejor opción)
- By the time we reached the station, the train (had left / had been leaving).
- She was exhausted because she (had studied / had been studying) all night.
- They cancelled the match because it (had rained / had been raining) for hours.
- When I called, he (had finished / had been finishing) his report.
- The floor was wet because someone (had spilled / had been spilling) water.
- We couldn’t enter; John (had forgotten / had been forgetting) the keys again.
- Her eyes were red because she (had cried / had been crying).
- By 2019, they (had opened / had been opening) three new branches.
- The teacher was annoyed; the students (had talked / had been talking) non-stop.
- He finally passed because he (had practiced / had been practicing) regularly.
B) Completa con past perfect simple o continuous (had + Vpp / had been + V-ing)
- By the time the guests arrived, we __________ (set) the table.
- She was sunburnt because she __________ (lie) on the beach all afternoon.
- I didn’t recognize him; he __________ (grow) a beard.
- The road was slippery; it __________ (snow) since dawn.
- We missed the intro because the movie __________ already __________ (start).
- They were bored; they __________ (wait) for the bus for 40 minutes.
- He apologized because he __________ (forget) her birthday.
- The kids were excited; they __________ (plan) the trip for weeks.
- My computer crashed after I __________ (install) the update.
- The garden was flooded; the sprinkler __________ (run) all night.
C) Transforma al tiempo correcto
Cambia las oraciones al pasado perfecto simple o continuo según corresponda.
- When we arrived, the show (already/start).
- She was nervous because she (not/practice) enough.
- They were dirty; they (paint) the fence.
- He was proud because he (win) the prize.
- The streets were wet; it (rain) all morning.
- I couldn’t call you; I (lose) my phone.
- Her hands hurt because she (type) for hours.
- By the end of the day, they (complete) the checklist.
D) Elige entre “when / by the time / after / before” y el tiempo correcto
- ________ we reached the venue, the band __________ (start).
- ________ she finished the marathon, she __________ (run) for nearly four hours.
- ________ they signed the contract, the lawyer __________ (review) every clause.
- ________ the bell rang, we __________ (pack) our bags.
- ________ I met Carla, I __________ (hear) a lot about her work.
- ________ the manager arrived, we __________ (discuss) the proposal for an hour.
E) Corrige el error (si lo hay)
- By the time I had arrived, they left.
- He had been finished the task before lunch.
- She was tired because she had worked since 6 a.m.
- It had been rained all day, so the match was postponed.
- They hadn’t been seeing the email before the meeting.
F) Completa en contexto (minitexto)
Yesterday was the school’s open day. By the time the parents arrived, the students __________ (prepare) their projects and the principal __________ already __________ (welcome) the first visitors. Some children were nervous because they __________ (rehearse) their presentations for only a week, but others were confident as they __________ (practice) for much longer. The science club room was crowded; it was obvious they __________ (work) hard on experiments. By the end of the event, everyone was happy because everything __________ (go) smoothly.
G) Empareja uso y explicación
Escribe Simple o Continuous según el énfasis más natural.
- Acción terminada antes de otra en pasado (resultado).
- Duración/actividad en progreso antes de otra en pasado (proceso).
- Cambio puntual de estado logrado (obtuvo el título).
- Causa de cansancio por actividad prolongada.
- Serie de logros completados antes de una fecha concreta.
7) Respuestas (Answer Key)
A) Opción múltiple
- had left
- had been studying
- had been raining
- had finished
- had spilled
- had forgotten
- had been crying
- had opened
- had been talking
- had been practicing / had practiced (ambas válidas según matiz; “had been practicing” enfatiza proceso)
B) Completa
- had set
- had been lying
- had grown
- had been snowing
- had started
- had been waiting
- had forgotten
- had been planning
- had installed
- had been running
C) Transformación (posibles soluciones)
- The show had already started when we arrived.
- She was nervous because she hadn’t practiced enough.
- They were dirty; they had been painting the fence.
- He was proud because he had won the prize.
- The streets were wet; it had been raining all morning.
- I couldn’t call you; I had lost my phone.
- Her hands hurt because she had been typing for hours.
- By the end of the day, they had completed the checklist.
D) Conectores + tiempos
- By the time we reached the venue, the band had started.
- When she finished the marathon, she had been running for nearly four hours.
- Before they signed the contract, the lawyer had reviewed every clause.
- When the bell rang, we had packed our bags. (también posible: By the time…)
- Before I met Carla, I had heard a lot about her work.
- By the time the manager arrived, we had been discussing the proposal for an hour.
E) Corrige el error
- By the time I arrived, they had left.
- He had finished the task before lunch. (no continuous con “finish”)
- Correcta, aunque también cabe continuous si se enfatiza duración: “had been working”.
- It had been raining all day, so the match was postponed.
- They hadn’t seen the email before the meeting. (simple para resultado)
F) Minitexto (solución ejemplo)
had prepared / had already welcomed / had been rehearsing / had been practicing / had been working / had gone
G) Empareja
- Simple
- Continuous
- Simple
- Continuous
- Simple
8) Trucos y errores frecuentes
1) Evita “had been + past participle” para acciones terminadas: usa had + Vpp (no “had been finished”).
2) Usa past perfect continuous para duración/causa (had been working) y past perfect simple para resultado (had finished).
3) Con by the time es muy frecuente el past perfect en la primera acción y past simple en la segunda.
4) Verbos de logro/estado puntual (finish, decide, arrive, win) suelen ir en past perfect simple.
5) Si dudas, pregúntate: ¿destaco el resultado (simple) o el proceso/duración (continuous)?

